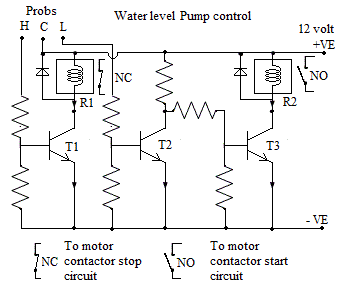
Water Pump Control With Tank Level
Introduction:- This circuit is designed to switch off water pump when water level is high in tank. When the water level in tank is below a set level it will start pump automatically.This circuit consist of three transistors and two relays with some Resistace etc it work on 12 volt supply. First relay R1 serves as stopping relay and ssecond relay R2 serves as starting relay. When water level goes below set level say 20 % of full tank start relay will pick up. With NO contact of R2 relay pump motor contactor will picks up and motor switch on. When tank will fill up completely first relay R1 will pick up with NC contact of first relay R1 pump motor contactor will switch off.
Senser:- There are three senser prob of conductive material is used. First one is common , second one is for high level and third one is for low level.
Circuit :- 12 volt supply is given to common prob. high level prob tip is set at a hight where pump is to be stop. When pump is running water level goes on increasing in tank. When water surface touches the high lebel prob the 12 volt of common prob will reach to high level prob. This high level prob is connected to base of transistor T1. With this transistor T1 will conduct and relay R1 will pick up. So the NC contact of relay R1 will open and pump contactor dropped out hence motor get stopped. With the use of water, tank water level goes on decreasing .When the water level decreases to a point where low level prob tip is placed the contact of water surface to prob will brake. As this prob is connected to base of transistor T2, the base volage of transistor T2 become zero hence transistor T2 will cut off. So collector voltage of transistor T2 become 5 volt so it will give base biasing to transistor T3. with the base biasing transistor T3 will conduct and relay R2 will picks up. With the NO contact of relay R2 motor contactor will picks up and hold on. After slightly fill up, the water level touch the low level prob so relay R2 drops down but pump will still runs continue because of motor contactor hold on. Again at high level pump will stop with relay R1.
https://vijayelectronicsforu.blogspot.com/2018/08/star-delta-starter-principle-circuit.html
https://vijayelectronicsforu.blogspot.com/2018/07/dc-motor-direction-control-by-two-relay.html